Double Opt-in
Contents
Definition
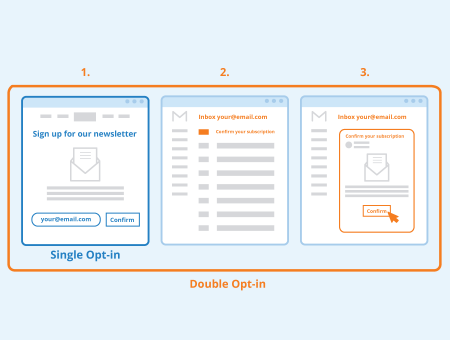
Double opt-in is a term used to describe a process through which a user subscribes to an email marketing list. In a double opt-in process, users sign up to a marketing list by providing their email address. They then receive an automated email that asks them to confirm the subscription, usually by clicking on a link provided within the message.
Double opt-in stands in contrast to a single opt-in, where a user only needs to provide their email once in order to subscribe to a marketing list. Single opt-in processes do not require confirmation, and subscription is immediate.
Procedure
Double opt-in is a three-step procedure.
- Step one: In the first step, the user enters their email address in a form or sign up box in order to subscribe to a newsletter, to receive offers or content upgrades, or to be added to a marketing list.
- Step two: The website operator processes the form and sends an email with a confirmation link to the specified email address.
- Step three: Once the user clicks on the confirmation link within the email, the subscription becomes effective. On the technical side, this procedure is usually carried out through the use of CRM software or marketing automation platforms
If the process ends after step 1, it is called a single opt-in.
Legal basis - is double opt-in required?
Where email marketing is concerned, businesses based in the United States are subject to the legal framework defined by CAN-SPAM Act 2003. Under this framework, double opt-in is not a legal requirement for commercial messaging. Communications addressed to customers in the state of California are governed by CCPA regulations, which do not require double opt-in either, but make opt-out mandatory.
Businesses in other countries, such as those based in the European Union, must adhere to data protection regulations of the relevant country and to GDPR rules. Double opt-in is not mandatory either, although permission to send emails is. In any case, using a two-step process is considered good practice. Marketers and business owners who engage in this type of communications must make sure they comply with certain guidelines. These are outlined in detail in section 4.
What to keep in mind when using double opt-in
Guidelines applying to commercial communications were created to protect the right of consumers against receiving unsolicited direct marketing messages. These communications should meet the following criteria to comply with that objective.
Detailed logging of consent
A user must give explicit and unambiguous consent to receiving email communications. Consent must also be given before an online business can collect personal data (for example via cookies). In addition, consent must be logged. Under GDPR (data protection regulations applicable to businesses in the European Union), consent logging must include details of time, date, and IP address.
Privacy policy
Messages sent in step 2 of the double opt-in procedure should include a link to the sender’s privacy policy. However, the user does not need to click on that link or acknowledge reading such a policy in order to confirm their subscription.
Allow anonymous registration
Once a user confirms his subscription to a mailing list, they are added to a database that is normally used for email marketing purposes. Users must be allowed to subscribe to that list anonymously, i.e. without entering personal data such as name, address, etc.
Content of the confirmation mail
The confirmation email that activates the subscription should include a call to action that explicitly requires the user to opt-in. These messages (and any subsequent communications) must also include an opt-out or unsubscribe option. Sender identity must be accurate and the subject line must reflect the purpose or content of the email body.
Advantages and disadvantages
Whether to use single or double opt-in is generally a matter of quality vs quantity. The two-step process may not be as effective as the single opt-in method if the goal is to grow a subscriber list fast, because users may forget to act on the confirmation email or delete it by mistake. Additionally, single opt-ins are usually suited to acquisition strategies, whereas double opt-ins focus more on retention.
Legal security
Using a double opt-in even in jurisdictions where it is not mandatory gives the marketer or business owner an additional layer of legal security. This is useful in the event that a user may raise a complaint or claim they never subscribed to the mailing list, as there will be a recorded log of the actions they took to subscribe.
Increased quality of your address list
Double opt-ins can reduce the likelihood of bots using spam addresses to subscribe to email services, which results in low deliverability and poor reach. On the other hand, users who go through both steps are more likely to have higher engagement with the brand, so this method can serve to generate quality leads and better open rates.
Increased technical effort
The growth in spambots and the malicious use of other people’s email addresses require additional technical actions to guarantee the user has a genuine interest in subscribing. For example, double opt-ins may be accompanied by captchas. Moreover, the procedure itself requires various technical elements, such as sign up forms, the automation of confirmation email, and database management.
Not every recipient of the verification email clicks on the confirmation link
A disadvantage of double opt-ins is that not every recipient acts on the confirmation request. This means that marketers risk losing subscribers who do not follow up and complete the process. The following suggestions can help optimize confirmation rates:
- Ensure the confirmation email is sent as quickly as possible after the initial sign up.
- Create a descriptive subject line.
- Place the confirmation call to action in a prominent place.
- Keep the message short and to the point.
- Provide an additional incentive for completing the confirmation, such as a discount on the first order or bonus content.
Related links
Similar articles
| About the author |
 |