Google Shopping
Contents
What is Google Shopping?
Google Shopping is an online service created so that internet users can search for products and compare the prices offered by different merchants. This service is meant to provide an on-the-spot shopping experience without having to browse through multiple sites. Google Shopping is free of charge and available in more than 120 countries worldwide.
One of its key features is personalization. Tailored product recommendations and promotions are available if the option is enabled in the user’s Google account settings. Moreover, Google Shopping as a service offers an added layer of confidence, since purchases are covered by Google’s guarantee, which applies to both well-known and lesser-known merchants. Along with this guarantee, shoppers can contact customer service for assistance with queries, shipping delays, and refund requests.
History and how it works
Google Shopping was launched in 2002 under the name of Froogle. Even in the early stages, its main functionality went beyond being a price comparison site, since the monetization model was different. Instead of relying on paid listings, it used the AdWords platform.
The service was renamed to Google Product Search in 2007. This was not only a name change but also highlighted the platform’s continuous improvements towards integration with Google’s search functionality. From then on, product listings were displayed simultaneously with search results.
In 2012, the service was rebranded as Google Shopping, and a few years later, the company announced that it would allow users to purchase products directly via the platform, as long as they were logged into their Google account. With this move, the service became a digital marketplace.
The platform works as follows: a user looking for a product enters its name in Google Search. On the results page, they can click on the Shopping tab located in the upper section, right under the search field. Doing this will display a list of products and their images, which can then be filtered by price, condition, seller, location, review score, etc. Once users click on an item, they will be directed to the merchant’s website to complete the transaction.
Alternatively, users can navigate to google.com/shopping and use the search function to look for a product. There is also a dedicated app that facilitates viewing listings and shopping for products from a mobile device. The app is called Google Shopping and also features an option to create product lists and view order history.
Product Listing Ads (PLAs)
With the 2012 rebranding came an important modification to the way merchants were allowed to submit product listings. Google implemented a pay-to-play model, in which paid listings and bidding were the main factors in getting the products to rank higher in search results. What this meant is that the platform effectively became an extension of the AdWords program, with ads displayed based on the product data submitted by the merchant, instead of keywords or text-based information.
The feature became known as Product Listing Ads, often abbreviated to PLAs. PLAs are essentially driven by a data feed. This enables merchants to upload detailed and structured product information so that shoppers can easily find what they are looking for. Once PLA data is submitted, Google displays the products based on user queries, featuring image and price.
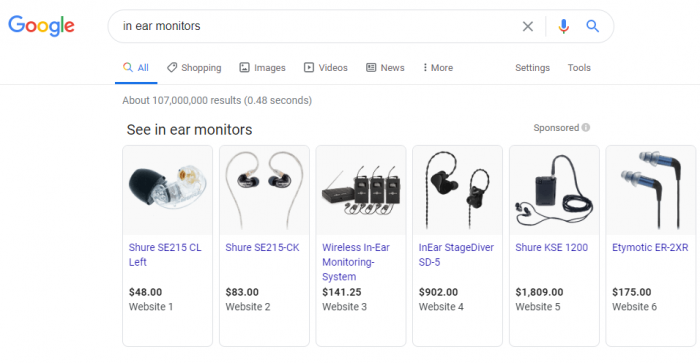
Screenshot with Product Listing Ads for the query "in-ear monitors" from google.com
You will need to use Google Ads to run a PLA campaign and manage the data feed. The procedure is detailed in section 5 below.
How to participate in Google Shopping
In order to advertise physical products, you will need to set up a Google Ads account and a Merchant Center account – this is the platform used to upload listings. Then you will need to link both accounts.
There are also content requirements and the need to comply with Google policies with respect to prohibited and restricted content or practices. These mainly refer to counterfeit or illegal goods, items that promote or enable dishonest behavior, misrepresentation, copyright infringement, and data collection practices.
Moreover, listing products on the platform requires setting up a PLA campaign, which in turn involves bidding using competitive auction models, and having a sufficient budget. To do this, you will need to calculate the maximum cost-per-click, which is the amount owed to Google each time someone clicks on a product.
Google Merchant Center
To start a PLA campaign, you will need to create a Google Merchant Center account using the credentials of your Google account. Some of the additional information required involves country, store name, and website.
Once logged into the Merchant Center (and assuming you have linked the account to Google Ads), you will be able to create a campaign. The procedure is similar to starting a Google Ads campaign in that it requires bidding and setting a daily budget, along with your desired target countries.
After the campaign is created, you can move on to the data feed and enter the information that will appear in the PLAs. This information must comply with Google’s product data specifications, particularly in what concerns basic attributes such as product ID, condition, title, price, description, links to your landing page, product’s image URL, availability, and brand.
Optimization of Google Shopping campaigns
In addition to compliance with product data specifications, the main visibility factors are bid amount and budget. If these are set too low, they may not generate enough traffic. However, there are ways to optimize your campaign. The most common include:
- Creating multiple campaigns.
- Optimizing images by ensuring they comply with or exceed quality guidelines.
- Optimizing product titles, descriptions, and categories.
- Setting different bids for different products, instead of using the same bid for all. This can be done in Google Ads by creating different product groups based on their condition, category, product type, etc. The principle is to identify the best sellers and increase the bid for those, and/or exclude non-profitable items.
- Using the geo-targeting functionality.
- Completing optional fields in the product data feed.
- Scheduling ads based on performance information, so they are displayed during the days or times of the day where they will get more views.
Importance for search engine optimization
Because the Shopping service is now integrated with Google’s search engine, using the platform allows for wider exposure of your products. To improve your search engine optimization efforts, you can also take advantage of the reporting tool, which allows merchants to assess their performance and make the necessary changes to improve results.
Although there is no direct connection between SEO and Google Shopping, these two aspects complement each other and can boost your digital marketing efforts. Both SEO and the Google Shopping platform can help you reach a wider audience, increase your website traffic numbers, and ultimately generate higher revenues.
Related links
- https://support.google.com/merchants/answer/7380908
- https://blog.hubspot.com/marketing/google-shopping
- https://blog.google/products/shopping/
Similar articles
| About the author |
 |