KPI
Contents
Definition
KPIs (Key Performance Indicators) are measurable metrics that can be used to ascertain an organization's performance and success against its strategic goals. Within the marketing context, KPIs are the performance measurements that would determine whether a campaign has been successful or not. Indicators need to be carefully selected to ensure that they accurately measure the performance areas that are being monitored.
What are KPIs used for?
The main purpose of KPIs is to create actionable strategies that are targeted towards improving a certain performance area. It creates a coherent action plan that can be used by all departments and personnel towards enabling an organization to meet its needs. In most cases, it is used to address a performance area that is underachieving.
For example, if a company is losing market share to its competitors, it could determine that this year's strategic goal is to increase its market share by 5%. The KPI that would be used to determine the success of this goal would be the market share data. The company would then have to look at its past strategic decisions and operating protocols for all departments to determine how this strategic goal can be met by improving the KPI.
KPIs are not standard across all organizations. Each organization, depending on its unique set of circumstances, will require different KPIs when measuring success. For example, a new entrant in the market will probably measure success by market share acquisition rather than profitability during its earlier years. A more entrenched player in the market might find it more appropriate to measure success by its customer retention rate. An organization that is courting investors will prioritize profitability. Success is relative, and it depends on the organization's short-term and long-term strategic goals.
Types of KPIs
There are many ways through which KPI's can be categorized. The most commonly used include:
Qualitative or quantitative indicators
Qualitative indicators are KPIs that cannot be measured by number (such as employee satisfaction) while quantitative indicators are KPIs that can be measured numerically (such as revenue).
Input, output, process, and outcome KPIs
All of these categorizations are related to the organizational process of creating value.
- Input: These are KPIs that are related to the resources that contribute to value creation. An example is the number of employees.
- Output: These are KPI's that are related to the created products (goods or services). They can be measured in terms of quantity, quality, or both. An example is the number of manufactured goods.
- Process: These are KPIs that are related to the activities involved to achieve the outcome and create value. An example is the time it takes to manufacture a single product.
- Outcome: These are KPIs related to the impact achieved by a strategic decision. An example is an increase in market share.
Leading and lagging KPIs
Leading KPIs are indicators that predict future performance while lagging indicators are used to review past performance. If, for example, the performance area under focus is the quality of provided services, the ratio of employees with proper academic qualifications can be used as a leading KPI. We would expect that a higher ratio of qualified employees would lead to better service delivery quality. Customer satisfaction can be seen as a lagging KPI for the quality of the provided service. A higher customer service score could indicate better service delivery quality.
Important steps in defining and using KPIs
KPIs need to be properly defined and utilized. Here are the three major steps that need to be taken to ensure that the implementation process achieves the expected results:
- The organization needs to have a clear objective before selecting the KPI(s) to be monitored. What type of success are they after – is it about growing the customer base or cutting down on unnecessary expenditure items?
- Having understood the objectives, the right indicators need to be selected. They need to be measurable and to correctly represent the performance areas being monitored.
- The strategy and KPIs need to be clearly communicated to the whole organization. Everybody needs to have the same definition of the KPI and understand their role in the adopted business strategy.
A method that has proven to be successful when determining KPIs is the SMART formula. SMART defines relevant KPIs as follows:
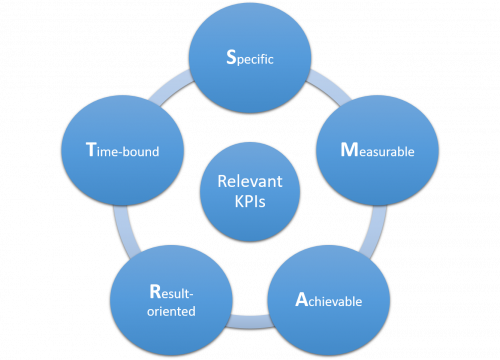
Figure: SMART formula for relevant KPIs, Author: Seobility
What are the risks involved in using KPIs?
KPI not linked to a company's goals
The whole purpose of measuring these performance indicators is to gauge how well a company is performing in terms of achieving its set goals. If the indicators chosen do not relate to the set goals, then the whole endeavor would be in vain.
Measuring useless KPI
Not all measurable data regarding a business are meaningful. Measuring a useless KPI is not only a waste of the organization's time and resources, but it also gives a false reading of the company's efforts to meet its key strategic goals.
Too much information
Too much information can be as harmful as having inadequate information. Measuring KPIs is just the first step, the data has to be analyzed and interpreted into an actionable strategic plan. When there is too much information, what is important gets lost in the clutter.
Established KPIs are not questioned and checked for relevance again
As an organization's internal and external environment changes, KPIs gain and lose relevance. A business needs to be vigilant in terms of ensuring that its measured KPIs are still relevant.
KPIs have to be updated when priorities change
No business has static priorities. These shift fluidly over time. A business needs to ensure that it is measuring key data that relate to its current priorities and not an outdated set of priorities.
Key figures for search engine optimization and online marketing
Click-through rate
The click-through rate measures the ratio of people who click on an online advertisement over the total number of people who viewed it. It measures the effectiveness of your online ad placement, design, and content.
Conversion rate
This is the ratio of people who respond to the stated call to action (make a purchase, sign up for a newsletter, etc) on your website over the total number of visitors.
Bounce rate
This is the ratio of people who leave your website (bounce) after viewing only one page over the total number of visitors. It measures how engaging your website is.
Organic visits
These are the visitors that come to your page from organic search engine results and not from clicking on paid advertisements. This measures the effectiveness of your SEO strategy.
Related links
- https://www.clicdata.com/blog/seo-kpis/
- https://www.seoworks.com/5-powerful-key-performance-indicators-must-count/
- https://www.clearpointstrategy.com/18-key-performance-indicators/
Similar articles
| About the author |
 |