Difference between revisions of "Pogo Sticking"
Ralph.ebnet (talk | contribs) |
|||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== What is pogo sticking? == | == What is pogo sticking? == | ||
| + | |||
| + | [[File:Pogo-Sticking.png|thumb|450px|right|alt=Pogo Sticking|'''Figure:''' Pogo Sticking - Author: Seobility - License: [[Creative Commons License BY-SA 4.0|CC BY-SA 4.0]]|link=https://www.seobility.net/en/wiki/images/d/d9/Pogo-Sticking.png]] | ||
Pogo sticking is when a searcher clicks on a search result and then goes back to the [[SERP|SERPs]] and moves on to the next one. This signals to [[Search Engine|search engines]] that the initial result didn’t provide the user with the content they were looking for. | Pogo sticking is when a searcher clicks on a search result and then goes back to the [[SERP|SERPs]] and moves on to the next one. This signals to [[Search Engine|search engines]] that the initial result didn’t provide the user with the content they were looking for. | ||
Pogo sticking is considered a negative signal as it shows search engines that a webpage didn’t satisfy the user’s [[Search Intent|intent]] or didn’t provide the information they were looking for. | Pogo sticking is considered a negative signal as it shows search engines that a webpage didn’t satisfy the user’s [[Search Intent|intent]] or didn’t provide the information they were looking for. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== What causes pogo sticking? == | == What causes pogo sticking? == | ||
| Line 55: | Line 53: | ||
[[Category:Search Engine Optimization]] | [[Category:Search Engine Optimization]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <html><script type="application/ld+json"> | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | "@context": "https://schema.org/", | ||
| + | "@type": "ImageObject", | ||
| + | "contentUrl": "https://www.seobility.net/en/wiki/images/d/d9/Pogo-Sticking.png", | ||
| + | "license": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/", | ||
| + | "acquireLicensePage": "https://www.seobility.net/en/wiki/Creative_Commons_License_BY-SA_4.0" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </script></html> | ||
Revision as of 11:45, 29 September 2021
Contents
What is pogo sticking?
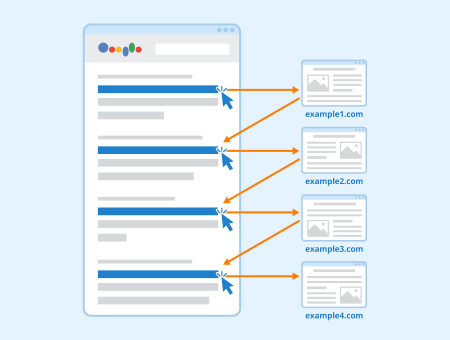
Pogo sticking is when a searcher clicks on a search result and then goes back to the SERPs and moves on to the next one. This signals to search engines that the initial result didn’t provide the user with the content they were looking for.
Pogo sticking is considered a negative signal as it shows search engines that a webpage didn’t satisfy the user’s intent or didn’t provide the information they were looking for.
What causes pogo sticking?
There can be various different things that cause pogo sticking, which can make it difficult to prevent. Below are a few things that may cause it:
- Thin content – Thin content can cause pogo sticking by not providing the user with the information they were after.
- Poor user experience – A poor user experience caused by, for example, a site that’s not optimized for mobile, spammy pop-ups, or an overall poor website design can cause a user to move to the next site.
- Slow site – A poor page speed can cause loading issues which can cause users to go back to the SERPs to try a different site.
- Doesn’t satisfy search intent – Even with high-quality content on a page, if the page doesn’t satisfy the search intent, pogo sticking can occur.
Pogo sticking and bounce rate
Bounce rate is a term that’s closely linked to pogo sticking, as a high bounce rate shows that a lot of people leave a page without viewing another page. However, a site’s bounce rate indicates the percentage of people that navigate away from the page without clicking through to any other pages but doesn’t give you any information about whether or not they go back and click on other results for the original search term.
A high bounce rate doesn’t necessarily indicate a low-quality page. If a website visitor finds all the information they were looking for on a page, a high bounce rate can actually be a positive signal as long as there is no pogo sticking.
How to reduce pogo sticking
A few things that can help to prevent pogo sticking include:
- Ensure a fast load time.
- Provide in-depth content.
- Optimize a page for the right keywords and the right search intent.
- Remove any spammy pop-ups.
- Keep content up to date.
- Implement an SSL certificate on the site.
- Use relevant internal links (high up) on the page.
Its relevance to SEO
Pogo sticking isn’t something that can be measured easily but it is something to be aware of when optimizing a website. It sends a clear negative signal to search engines, making it more difficult to rank a page or potentially moving the page down in the SERPs.
Proper on-page SEO can help reduce pogo sticking by ensuring a good user experience and providing in-depth content on all pages. Optimizing your pages for the right keywords can also help reduce pogo sticking by ensuring a site’s pages are relevant to the search term and the search intent behind it.
Related links
Similar articles