Difference between revisions of "REST API"
Ralph.ebnet (talk | contribs) (→Client-server architecture) |
(→Related links) |
||
| (3 intermediate revisions by one other user not shown) | |||
| Line 1: | Line 1: | ||
| − | <seo title="What is REST API?" metadescription=" | + | <seo title="What is a REST API? Definition and Principles" metadescription="API is the acronym for Application Programming Interface. It allows two applications to communicate with each other. Learn more ..."/> |
== Definition and function == | == Definition and function == | ||
| Line 32: | Line 32: | ||
=== Caching === | === Caching === | ||
| − | The client, server, and any intermediate components can cache all resources to improve performance. The information can be classified as cacheable or non-cacheable. | + | The client, server, and any intermediate components can [[Caching|cache]] all resources to improve performance. The information can be classified as cacheable or non-cacheable. |
=== Uniform interface === | === Uniform interface === | ||
| Line 69: | Line 69: | ||
} | } | ||
</script></html> | </script></html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:left" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |'''About the author''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[File:Seobility S.jpg|link=|100px|left|alt=Seobility S]] The Seobility Wiki team consists of seasoned SEOs, digital marketing professionals, and business experts with combined hands-on experience in SEO, online marketing and web development. All our articles went through a multi-level editorial process to provide you with the best possible quality and truly helpful information. Learn more about <html><a href="https://www.seobility.net/en/wiki/Seobility_Wiki_Team" target="_blank">the people behind the Seobility Wiki</a></html>. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <html><script type="application/ld+json"> | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | "@context": "https://schema.org", | ||
| + | "@type": "Article", | ||
| + | "author": { | ||
| + | "@type": "Organization", | ||
| + | "name": "Seobility", | ||
| + | "url": "https://www.seobility.net/" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </script></html> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:12, 6 December 2023
Contents
Definition and function
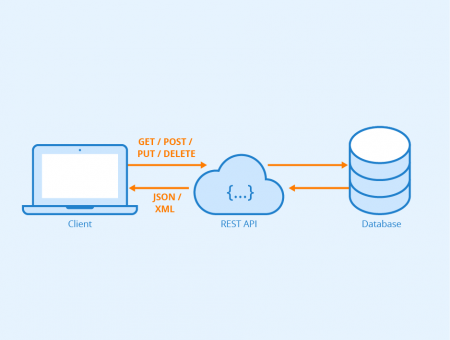
API is the acronym for "Application Programming Interface". It is a software that allows two applications to communicate with each other over the internet and through various devices. Every time you access an app like Facebook or check the weather on your smartphone, an API is used.
The abbreviation REST stands for "Representational State Transfer" and refers to a software architectural style. It is based on six principles that describe how networked resources are defined and addressed on the web, for example in a cloud.
These principles were described by Roy Fielding in his dissertation "Architectural Styles and the Design of Network-based Software Architectures" in 2000. The principle of statelessness is essential for a REST API. It states that each REST message contains all the information necessary to understand that message. REST is not a programming language or basic structure and is not a piece of software that can be executed.
RESTful APIs use the HTTP request methods GET, POST, PUT and DELETE defined in RFC 2616. Therefore, no protocol conventions are required for client and server to communicate with each other via REST-APIs. With GET, resources are queried from a RESTful API. POST is used to update or change the state of a resource. With PUT, new resources can be created or the content of existing resources can be replaced. DELETE is used to delete resources. These four HTTP methods are usually sufficient to cover most use cases.
Origin and evolution of REST APIs
REST is an alternative to methods such as SOAP (Simple Object Access Protocol) and WSDL (Web Services Description Language). It was developed towards the end of the 1990s and fundamentally changed the API landscape. The first companies to use a REST API were eBay and Amazon. Only a selection of partners got access to eBay’s well documented and user-friendly REST API. As a result, eBay’s marketplace was not only accessible through direct visits but through any website that accessed the eBay API.
Flickr also launched a REST API in 2004, just in time for the rise of social networking and blogs on the web. This paved the way for social sharing, which Facebook and Twitter later joined.
In 2006, Amazon’s REST API helped contribute to the development of the cloud, which is now widely used. RESTful APIs allow users to connect to the cloud and interact with cloud services. They are now accessed by many websites and are considered the backbone of the web.
The six principles of REST
Client-server architecture
The principle behind the client-server architecture is the separation of problems. Dividing the user interface from data storage improves the portability of that interface across multiple platforms. It also has the advantage that different components can be developed independently from each other.
Statelessness
Statelessness means that the communication between client and server always contains all the information needed to execute the request. There is no session state on the server, it is kept entirely on the client. If access to a resource requires authentication, the client must authenticate itself on each request.
Caching
The client, server, and any intermediate components can cache all resources to improve performance. The information can be classified as cacheable or non-cacheable.
Uniform interface
All components of a RESTful API have to follow the same rules to communicate with each other. This also makes it easier to understand interactions between the various components of a system.
Layered system
Individual components cannot see beyond the immediate level they interact with. This means that a client that connects to an intermediate component such as a proxy does not know what is behind it. Therefore, components can be easily exchanged or expanded independently of each other.
Code-on-demand
Additional code can be downloaded to extend client functionality. However, this is optional because the client may not be able to download or execute this code.
The advantage of REST for the development of an API
The complete separation of the user interface from server and data storage offers some advantages for the development of an API. For example, it improves the portability of the interface to other types of platforms, increases project scalability and allows different components to be developed independently. Developers can easily migrate to other servers or make changes to the database, provided the data is sent correctly from each request. The separation thus increases overall flexibility in development.
A REST API is always independent of the type of platform or languages used, it adapts to the type of syntax or platform used. This provides great freedom when changing or testing new environments within a development. You can use PHP, Java, Python or Node.js servers with a REST API. Only responses to requests must be in the language used for information exchange, usually XML or JSON.
One disadvantage of REST APIs is the lack of standardization, which can lead to misunderstandings.
Related links
| About the author |
 |