Difference between revisions of "Soft 404"
(→Similar articles) |
|||
| (4 intermediate revisions by 2 users not shown) | |||
| Line 2: | Line 2: | ||
== What is a soft 404? == | == What is a soft 404? == | ||
| + | [[File:Soft-404.png|thumb|450px|right|alt=Soft 404|'''Figure:''' Soft 404 - Author: Seobility - License: [[Creative Commons License BY-SA 4.0|CC BY-SA 4.0]]|link=https://www.seobility.net/en/wiki/images/4/43/Soft-404.png]] | ||
| − | A soft 404 is when a page doesn’t exist according to a website, but still returns a 200 response code (successful HTTP request). This could happen when a webmaster creates a 404 “page not found” page without returning a 404 response code for example, indicating to visitors that the page does not exist but | + | A soft 404 is when a page doesn’t exist according to a website, but still returns a 200 response code (successful HTTP request). This could happen when a webmaster creates a 404 “page not found” page without returning a 404 response code, for example, indicating to visitors that the page does not exist but |
indicating to [[Search Engine|search engines]] that the page does exist. | indicating to [[Search Engine|search engines]] that the page does exist. | ||
| − | Although a soft 404 is generally considered damaging to a site’s search engine performance, pages that are | + | Although a soft 404 is generally considered damaging to a site’s search engine performance, pages that are labeled as soft 404s can also be general [[Thin Content|thin content]] pages or pages with no content on them. Although this isn’t technically a soft 404, it’s still important to fix them as they can also harm your performance in the search engines. |
== The difference between a normal 404 and a soft 404 == | == The difference between a normal 404 and a soft 404 == | ||
| Line 14: | Line 15: | ||
A website that returns a 404 response code often has a custom 404 error page, which tells users that a page doesn’t exist and often links to other pages that may be useful to them instead. This helps to improve the [[User Experience|user experience]] by preventing dead ends and serving alternative pages that may be beneficial to users. | A website that returns a 404 response code often has a custom 404 error page, which tells users that a page doesn’t exist and often links to other pages that may be useful to them instead. This helps to improve the [[User Experience|user experience]] by preventing dead ends and serving alternative pages that may be beneficial to users. | ||
| − | Soft 404 pages commonly serve the same 404 page to users but return a 200 response code, indicating to search engines that the page is a real page on the site. This can cause thin content and [[Duplicate Content|duplicate content]] issues, index bloat and/or wasted crawl budget, potentially damaging a site’s SEO performance. | + | Soft 404 pages commonly serve the same 404 page to users but return a 200 response code, indicating to search engines that the page is a real page on the site. This can cause thin content and [[Duplicate Content|duplicate content]] issues, index bloat, and/or wasted crawl budget, potentially damaging a site’s SEO performance. |
| − | [[File:Soft-404-example.png|link=|border|alt=Soft 404|Screenshot showing a 404 page]] | + | [[File:Soft-404-example.png|link=|border|alt=Soft 404 Screenshot|Screenshot showing a 404 page]] |
An example of a 404 page on [https://www.forbes.com Forbes] that mitigates dead ends by linking to other articles and allowing users access to the menu and search bar. | An example of a 404 page on [https://www.forbes.com Forbes] that mitigates dead ends by linking to other articles and allowing users access to the menu and search bar. | ||
| Line 23: | Line 24: | ||
There are a few common ways to find soft 404s on a website. The first is to use [[Google Search Console|Google Search Console]], which flags soft 404s it discovers. This shows you all pages that Google has flagged as soft 404s, allowing you to fix them. | There are a few common ways to find soft 404s on a website. The first is to use [[Google Search Console|Google Search Console]], which flags soft 404s it discovers. This shows you all pages that Google has flagged as soft 404s, allowing you to fix them. | ||
| − | Another common method used to find soft 404s is by using a crawling tool, like our [https://www.seobility.net/en/seocheck/ SEO checker]. [[On-Page SEO|On-page SEO]] tools show you the status codes that different pages return, allowing you to browse through them to find any pages that should be providing a 404 code instead of a 200 code. | + | Another common method used to find soft 404s is by using a crawling tool, like our [https://www.seobility.net/en/seocheck/ SEO checker]. [[On-Page SEO|On-page SEO]] tools show you the [[HTTP Status Code|status codes]] that different pages return, allowing you to browse through them to find any pages that should be providing a 404 code instead of a 200 code. |
== Fixing soft 404s == | == Fixing soft 404s == | ||
| Line 37: | Line 38: | ||
=== Optimize the page === | === Optimize the page === | ||
| − | If the page is a real page that’s incorrectly creating a soft 404 error, improving the quality of the page can remove the error. It is rare for search engines to incorrectly mark a page as a soft 404 page, but if it does happen then this can be a good way to solve it. | + | If the page is a real page that’s incorrectly creating a soft 404 error (e.g. because of thin content), improving the quality of the page content can remove the error. It is rare for search engines to incorrectly mark a page as a soft 404 page, but if it does happen then this can be a good way to solve it. |
== SEO implications of soft 404s == | == SEO implications of soft 404s == | ||
| − | Soft 404s can cause a range of SEO issues. If there are many identical pages returning 200 codes, for example due to the fact a site’s “404 – page not found” pages are returning 200 status codes, this could cause duplicate content issues on a site, reducing a | + | Soft 404s can cause a range of SEO issues. If there are many identical pages returning 200 codes, for example, due to the fact a site’s “404 – page not found” pages are returning 200 status codes, this could cause duplicate content issues on a site, reducing a site's quality in the eyes of search engines. This same problem can also cause thin content issues since 404 pages commonly have either no content at all or very little content. |
| + | |||
| + | Index bloat and wasted crawl budget are two other important SEO issues that soft 404s can cause. Since search engine crawlers spend time crawling soft 404 pages and they may be indexed if they are not immediately flagged as soft 404s, soft 404s harm your site’s overall SEO by taking focus away from the real pages on a website. If there are backlinks pointing to the soft 404 pages, [[Link Juice|link juice]] could be wasted which also harms the possibility for other content on your site to rank. | ||
| − | |||
| − | |||
== Related links == | == Related links == | ||
| Line 57: | Line 58: | ||
[[Category:Search Engine Optimization]] | [[Category:Search Engine Optimization]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | <html><script type="application/ld+json"> | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | "@context": "https://schema.org/", | ||
| + | "@type": "ImageObject", | ||
| + | "contentUrl": "https://www.seobility.net/en/wiki/images/4/43/Soft-404.png", | ||
| + | "license": "https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by-sa/4.0/", | ||
| + | "acquireLicensePage": "https://www.seobility.net/en/wiki/Creative_Commons_License_BY-SA_4.0" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </script></html> | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:left" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |'''About the author''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[File:Seobility S.jpg|link=|100px|left|alt=Seobility S]] The Seobility Wiki team consists of seasoned SEOs, digital marketing professionals, and business experts with combined hands-on experience in SEO, online marketing and web development. All our articles went through a multi-level editorial process to provide you with the best possible quality and truly helpful information. Learn more about <html><a href="https://www.seobility.net/en/wiki/Seobility_Wiki_Team" target="_blank">the people behind the Seobility Wiki</a></html>. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <html><script type="application/ld+json"> | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | "@context": "https://schema.org", | ||
| + | "@type": "Article", | ||
| + | "author": { | ||
| + | "@type": "Organization", | ||
| + | "name": "Seobility", | ||
| + | "url": "https://www.seobility.net/" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </script></html> | ||
Latest revision as of 17:23, 6 December 2023
Contents
What is a soft 404?
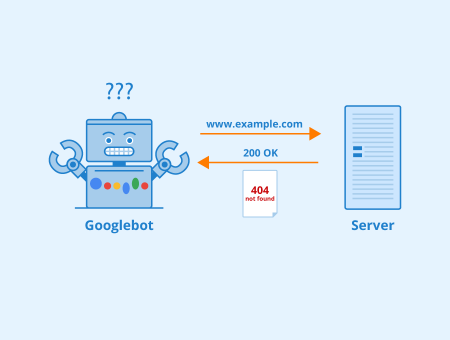
A soft 404 is when a page doesn’t exist according to a website, but still returns a 200 response code (successful HTTP request). This could happen when a webmaster creates a 404 “page not found” page without returning a 404 response code, for example, indicating to visitors that the page does not exist but indicating to search engines that the page does exist.
Although a soft 404 is generally considered damaging to a site’s search engine performance, pages that are labeled as soft 404s can also be general thin content pages or pages with no content on them. Although this isn’t technically a soft 404, it’s still important to fix them as they can also harm your performance in the search engines.
The difference between a normal 404 and a soft 404
A 404-response code is a response code provided by a website’s server that indicates that a page does not exist. This helps search engines understand not to crawl or index a page, reducing index bloat (all irrelevant pages indexed by search engines) and sparing crawl budget.
A website that returns a 404 response code often has a custom 404 error page, which tells users that a page doesn’t exist and often links to other pages that may be useful to them instead. This helps to improve the user experience by preventing dead ends and serving alternative pages that may be beneficial to users.
Soft 404 pages commonly serve the same 404 page to users but return a 200 response code, indicating to search engines that the page is a real page on the site. This can cause thin content and duplicate content issues, index bloat, and/or wasted crawl budget, potentially damaging a site’s SEO performance.
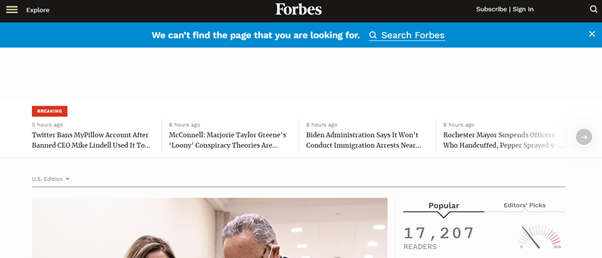
An example of a 404 page on Forbes that mitigates dead ends by linking to other articles and allowing users access to the menu and search bar.
How to find soft 404s
There are a few common ways to find soft 404s on a website. The first is to use Google Search Console, which flags soft 404s it discovers. This shows you all pages that Google has flagged as soft 404s, allowing you to fix them.
Another common method used to find soft 404s is by using a crawling tool, like our SEO checker. On-page SEO tools show you the status codes that different pages return, allowing you to browse through them to find any pages that should be providing a 404 code instead of a 200 code.
Fixing soft 404s
Return the correct response code
If the page doesn’t exist, then ensuring it returns a 404 response code instead of a 200 response code will remove the soft 404 issue.
Redirect the page
If the page has moved or there is another page on your site that covers the same topic, website owners may choose to redirect the page, eliminating the soft 404 issue. This method is more commonly used when there are valuable backlinks pointing to the soft 404 page.
Optimize the page
If the page is a real page that’s incorrectly creating a soft 404 error (e.g. because of thin content), improving the quality of the page content can remove the error. It is rare for search engines to incorrectly mark a page as a soft 404 page, but if it does happen then this can be a good way to solve it.
SEO implications of soft 404s
Soft 404s can cause a range of SEO issues. If there are many identical pages returning 200 codes, for example, due to the fact a site’s “404 – page not found” pages are returning 200 status codes, this could cause duplicate content issues on a site, reducing a site's quality in the eyes of search engines. This same problem can also cause thin content issues since 404 pages commonly have either no content at all or very little content.
Index bloat and wasted crawl budget are two other important SEO issues that soft 404s can cause. Since search engine crawlers spend time crawling soft 404 pages and they may be indexed if they are not immediately flagged as soft 404s, soft 404s harm your site’s overall SEO by taking focus away from the real pages on a website. If there are backlinks pointing to the soft 404 pages, link juice could be wasted which also harms the possibility for other content on your site to rank.
Related links
- https://developers.google.com/search/blog/2010/06/crawl-errors-now-reports-soft-404s
- https://www.searchenginejournal.com/404-errors-google-crawling-indexing-ranking/261541/
- https://developers.google.com/search/docs/advanced/crawling/soft-404-errors
Similar articles
| About the author |
 |