Difference between revisions of "Redirect"
(→Server-side redirects) |
Ralph.ebnet (talk | contribs) (→Server-side redirects) |
||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
[[File:WWW-Redirect.png|thumb|450px|right|alt=redirect|'''Figure:''' Redirect - Author: Seobility - License: [[Creative Commons License BY-SA 4.0|CC BY-SA 4.0]]|link=https://www.seobility.net/en/wiki/images/2/2c/WWW-Redirect.png]] | [[File:WWW-Redirect.png|thumb|450px|right|alt=redirect|'''Figure:''' Redirect - Author: Seobility - License: [[Creative Commons License BY-SA 4.0|CC BY-SA 4.0]]|link=https://www.seobility.net/en/wiki/images/2/2c/WWW-Redirect.png]] | ||
| − | Server-side redirects (HTTP redirects) are redirects that use the status codes 3xx. The returned status messages can also be understood by [[Search Engine Crawlers|web crawlers]] such as Googlebot. | + | Server-side redirects (HTTP redirects) are redirects that use the status codes 3xx. The returned status messages can also be understood by [[Search Engine Crawlers|web crawlers]] such as [[Googlebot]]. |
* 301-Redirect: Provides a way to permanently redirect a URL. | * 301-Redirect: Provides a way to permanently redirect a URL. | ||
Revision as of 15:40, 6 October 2019
Contents
Definition
The term redirect means that users are automatically directed to web page B when calling up web page A without having to make any entries. This means that an internet user navigates to a certain URL, but is redirected to another page within the existing domain or to a new domain. Depending on how the redirect is configured, this can happen immediately or after a defined period of time. Internet users have no direct influence on the redirect.
You can distinguish between legitimate and malicious redirects. A legitimate redirect is caused, for example, by moving an existing website to a new domain. Visitors are automatically redirected to the correct website so that they do not suffer any disadvantages.
However, a malicious redirect aims to lead visitors to a website that they did not actually want to visit. This form of redirect is considered abuse and is primarily used by cybercriminals to navigate unsuspecting internet users to dubious websites. These two types of redirects have different effects. Search engines like Google can detect a malicious redirect effectively, mark it as spam, and remove it from the index.
A redirect is realized either from the server-side or from the client-side. It depends on the specific application scenario which option is suited best. However, search engines generally recommend the use of server-side redirects.
Server-side redirects
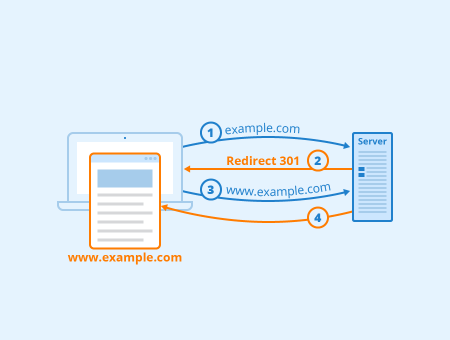
Server-side redirects (HTTP redirects) are redirects that use the status codes 3xx. The returned status messages can also be understood by web crawlers such as Googlebot.
- 301-Redirect: Provides a way to permanently redirect a URL.
- 302-Redirect: With this redirect, web pages in HTTP version 1.0 were permanently redirected.
- 307-Redirect: With the 307-Redirect, short-term redirects can be implemented.
Usually, users don’t notice a server-side redirection unless they take a closer look at their browser’s address bar. Without a redirect, visitors would get the error message 404 "This website does not exist" or an outdated version of an already moved website. Server-side redirects can be realized on Apache web servers with an .htaccess file or with the scripting language PHP. For example, a 301 redirect can be implemented with the following code in the .htaccess file:
RewriteEngine on
RewriteCond %{HTTP_HOST} ^example.com [NC]
RewriteRule ^(.*)$ http://www.example.com/$1 [R=301,NC]
With the code above, users entering a domain name without “www” can be automatically redirected to the version with www, thus avoiding duplicate content.
Client-side redirects
Client-side redirects are implemented directly in the website’s source code so that no changes need to be made to the server. These redirects can be realized in two ways: via a meta refresh tag or via JavaScript. In principle, however, you should avoid using client-side redirects, as Google and other search engines sometimes can not interpret them correctly. In the worst case, they can even have a negative effect on search engine optimization.
A client-side forwarding via meta refresh can be implemented with the following meta tag:
meta http-equiv="refresh" content="0;url=http://www.example.com/"
A meta refresh is thus executed through the user’s browser. Although this type of redirect is relatively easy to implement, it has some disadvantages in terms of usability and search engine optimization. For example, visitors have to wait a few seconds until they are redirected to the new URL.
Client-side redirects via JavaScript are only recommended to a limited extent as they require JavaScript to be activated in the user's web browser. In addition, Google and other search engines may interpret this type of redirect as a manipulation attempt, which could have negative SEO consequences. Redirecting via JavaScript can be realized in the following way:
document.location.href = 'new-index.html'
Benefits and importance for SEO
Used correctly, redirects can have a positive effect on search engine optimization. However, to implement a redirect correctly, it is important to know the different HTTP status codes and their influence on web crawlers. From an SEO point of view, only the use of server-side redirects makes sense, since the status codes can be specified in the .htaccess file. In particular, 301 redirects are recommended here, since the link equity of a page can be fully passed on with these.
Redirects can be useful for SEO and the usability of a website in many ways:
- Dead links can be redirected to a new domain via a 301 redirect.
- With a permanent redirect (301), web pages can be redirected from a URL without www. to the version with www., thus avoiding duplicate content.
- By using 307 redirects, website visitors can be made aware of server maintenance work.