Difference between revisions of "Character Encoding"
(→Why different character sets are necessary) |
|||
| Line 15: | Line 15: | ||
== Which encoding should you choose? == | == Which encoding should you choose? == | ||
| − | The US-ASCII character set is sufficient for an English-language website if typographically correct punctuation, such as curly quotation marks, is not required. For other European languages such as German, French or Spanish, the ISO 8859-1 character set works very well, which is why it has become a de facto standard for Western Europe. Character sets with Polish, Czech, Cyrillic or Greek characters can choose a different version from ISO 8859. Even encoding Hebrew, Arabic and Oriental characters on a web page is no problem if UTF-8 is selected for character encoding. This abbreviation stands for UCS Transformation Format - 8 Bit, where UCS is the abbreviation for Universal Character Set. | + | The US-[[ASCII]] character set is sufficient for an English-language website if typographically correct punctuation, such as curly quotation marks, is not required. For other European languages such as German, French or Spanish, the ISO 8859-1 character set works very well, which is why it has become a de facto standard for Western Europe. Character sets with Polish, Czech, Cyrillic or Greek characters can choose a different version from ISO 8859. Even encoding Hebrew, Arabic and Oriental characters on a web page is no problem if UTF-8 is selected for character encoding. This abbreviation stands for UCS Transformation Format - 8 Bit, where UCS is the abbreviation for Universal Character Set. |
UTF-8 has become the most commonly used character encoding. It uses the code table of the Unicode system, which contains the characters and elements of all known font cultures determined by linguists. In Unicode, the numbers of the characters are represented by a number two bytes in size. In this way, up to 65536 characters can be placed in that code table. For this reason, UTF-8 is the most commonly used character set on the internet. | UTF-8 has become the most commonly used character encoding. It uses the code table of the Unicode system, which contains the characters and elements of all known font cultures determined by linguists. In Unicode, the numbers of the characters are represented by a number two bytes in size. In this way, up to 65536 characters can be placed in that code table. For this reason, UTF-8 is the most commonly used character set on the internet. | ||
Revision as of 16:48, 12 March 2019
Contents
Definition
In order to display letters, numbers, and symbols, a computer needs a character repertoire. For practical use, this set of characters is arranged and numbered in a specific order. This ordered repertoire of characters is called a character set. In order for computers to recognize the characters correctly, they are also described by a pattern of bits, which is called character encoding. Since the character set already specifies a certain sequence and numbering, the bit patterns only have to be assigned to the characters in order to create the character encoding.
Character encoding is relevant for HTML documents since these are always stored with a specific type of character encoding. This allows a unique assignment of letters, numbers, and symbols of a character set. The information about the form of encoding used for a file is sent to browsers or other user agents when it is opened so that the bits and bytes can be interpreted into characters correctly. If the declared character encoding does not match the one actually used, browsers cannot display the content of a website correctly and search engines can’t make use of such pages either.
Why different character sets are necessary
Selecting a specific character set determines the range of characters that can be used on a web page. Normal Latin letters are rarely a problem, but some languages require more letters than others or use characters such as dots, checkmarks, dashes, circles or arcs above or below the letters.
This can lead to problems if a character is required that cannot be represented by the selected encoding. In this case, a symbolic paraphrase (entity reference) must be used in the HTML code. For example, the entity reference © represents the symbol ©. Entity references begin with a "&" and end with a semicolon ";". While the use of references usually works relatively well, the process requires more bytes, complicates markup, and often leads to typos, so their use in the HTML code should be kept to a minimum.
Which encoding should you choose?
The US-ASCII character set is sufficient for an English-language website if typographically correct punctuation, such as curly quotation marks, is not required. For other European languages such as German, French or Spanish, the ISO 8859-1 character set works very well, which is why it has become a de facto standard for Western Europe. Character sets with Polish, Czech, Cyrillic or Greek characters can choose a different version from ISO 8859. Even encoding Hebrew, Arabic and Oriental characters on a web page is no problem if UTF-8 is selected for character encoding. This abbreviation stands for UCS Transformation Format - 8 Bit, where UCS is the abbreviation for Universal Character Set.
UTF-8 has become the most commonly used character encoding. It uses the code table of the Unicode system, which contains the characters and elements of all known font cultures determined by linguists. In Unicode, the numbers of the characters are represented by a number two bytes in size. In this way, up to 65536 characters can be placed in that code table. For this reason, UTF-8 is the most commonly used character set on the internet.
Basically, it would make sense to always use UTF-8 instead of dealing with entities in the HTML code. Unfortunately, this is not always possible, because not all editors support UTF-8. In addition, some older browsers do not understand UTF-8, although this problem shouldn’t occur too often nowadays.
How to specify the character encoding in your document
Once you've chosen an encoding, you need to make sure that the right information is passed to browsers and search engines. In every HTML document, you must specify the character encoding used. For this, you can use either the HTTP header or HTML code.
Specification in the HTTP header
Web pages are provided via HyperText Transfer Protocol (HTTP). Browsers send a request via HTTP and servers send a response back via HTTP. This response consists of two parts: the HTTP header and the body, separated by a blank line. The headers contain information about the body (content). The body then consists of the requested resource, usually an HTML document. The encoding information for this document is sent by a web server via the content type header:
Content-Type: text/html; charset=utf-8
Specification in HTML code
If you want to provide the HTTP equivalent in HTML code, you can use a meta element in the HEAD section of your document:
<meta http-equiv="Content-Type" content="text/html; charset=utf-8">
Alternatively, you can use the following meta element in your HTML code:
<meta charset="utf-8">
Here’s an example for the specification of character encoding in HTML code:
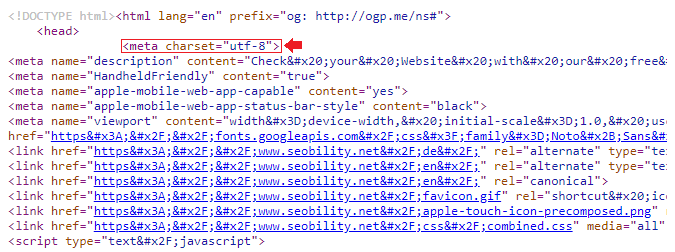
Screenshot with character encoding in HTML code from seobility.net
Note, however, that each HTTP header overwrites a meta element in HTML code, which is why the web server must be set up correctly. For an Apache server, the following code has to be written into the configuration file:
AddDefaultCharset UTF-8
For Microsoft IIS, this setting must be specified in numerous dialog boxes.
For XML, you should specify the encoding in the header of your file. XML only supports UTF-8 and UTF-16, which greatly simplifies selection:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="utf-8"?/>
Summary
The choice of an appropriate character encoding is essential if you want to make sure that your website is displayed correctly. If you select a character set that is unsuitable for your website, such as ISO 8859-1 for a Chinese website, you will have to use many entities in your HTML code, which unnecessarily increases file size.
Therefore you should generally use UTF-8 for multilingual websites. UTF-8 and the ISO 8859 series are supported by all modern web browsers. Most browsers also support some other encodings, but if an unusual one is chosen, you run the risk that some visitors, including search engines, may not be able to read your content.