Difference between revisions of "Mod Rewrite"
Ralph.ebnet (talk | contribs) (→The power of flexible URLs) |
|||
| Line 8: | Line 8: | ||
== The power of flexible URLs == | == The power of flexible URLs == | ||
| − | Administrators and architects of complex web systems often work with the "mod_rewrite" module, because it | + | Administrators and architects of complex web systems often work with the "mod_rewrite" module, because it allows easy rewriting of URLs. Particularly for rewriting dynamic addresses into [[SEO-friendly URLs]], mod_rewrite is often used. |
== The rewrite engine == | == The rewrite engine == | ||
Revision as of 15:25, 24 September 2020
Contents
Definition
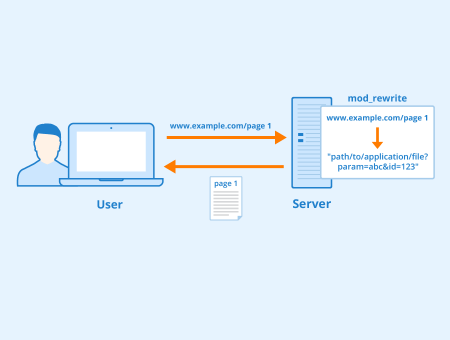
The term "mod_rewrite" refers to a module for the Apache web server, which “rewrites” or redirects requests to specified content. Basically, the module transforms incoming requests to a path in the web server's file system. This makes it possible to "rewrite" a URL. For this, a "rewriterule" is defined, which controls this rewriting and is realized with the help of regular expressions.
The power of flexible URLs
Administrators and architects of complex web systems often work with the "mod_rewrite" module, because it allows easy rewriting of URLs. Particularly for rewriting dynamic addresses into SEO-friendly URLs, mod_rewrite is often used.
The rewrite engine
Behind the rewrite module implementation lies a complex rewrite engine. This means that dedicated software receives the text-based rules defined in a web server's .htaccess file and interprets them so that the server can implement those rules. The rewrite engine can process a number of conditions for each rule. It always considers the entire URL, which is also called URI (Unified Resource Identifier).
Various configuration files such as httpd.conf are available on the web server for setting up rewrite rules. In most cases, however, these rules are specified in the server’s .htaccess file for standardization purposes.
Directives
The rewrite module's functionality is controlled by directives. These specifications form sections within the web server's configuration that initiate functions and allow a clear and separate configuration, for example, for different URLs or different paths. The basis for the display of individual directives is XML semantics. One of the most well-known and frequently used applications is the rewrite base directive. It specifies which relative path to replace by a rewrite rule.
There are also other directives, for example, to map conditions. This allows you to arrange complex rules for web presences. To avoid conflicting or non-compliant rules, you should make sure that it is always comprehensible which rules have been set.
Example
There are numerous scenarios for using the mod_rewrite module in Apache. Many expressions are therefore published for standard cases and can be used by any administrator. An example of a rewrite rule is:
RewriteEngine on RewriteRule (.*)\.html$ /cgi-bin/script.pl?var=$1
The rule's semantics are based on regular expressions. They can be understood as a kind of "search and replace". This means that incoming strings are checked and rewritten.
In the example above, all accesses to the HTML file are found in the Apache web server's base directory. No other input is processed by this rewrite rule.
All inputs that meet this condition are redirected to a script. It does not matter with which URL or URI it is accessed. The script also passes the name of the originally called path.
This example shows that the rewrite module is suitable for controlling complex applications on web servers and beyond.
Importance for SEO
Rewriteengine is very important for search engine optimization because the routines of search engines are designed to find well structured and human-readable URL trees.
However, many web applications generate dynamic URLs that humans cannot logically comprehend and which do not reveal anything about a website's structure.
This problem can be solved with the Apache module mod_rewrite by converting complex dynamic URLs into readable URLs. This makes it easier for both users and search engines to understand the structure of a website. As a result, users can judge what they will find on a page and whether it is relevant for them on the basis of a search result’s URL in the SERPs.
Related links
Similar articles