Difference between revisions of "Google Cache"
(→Similar articles) |
(→Similar articles) |
||
| Line 96: | Line 96: | ||
|'''About the author''' | |'''About the author''' | ||
|- | |- | ||
| − | | [[File:Seobility S.jpg|link=|100px|left|alt=Seobility S]] The Seobility Wiki team consists of | + | | [[File:Seobility S.jpg|link=|100px|left|alt=Seobility S]] The Seobility Wiki team consists of seasoned SEOs, digital marketing professionals, and business experts with combined hands-on experience in SEO, online marketing and web development. All our articles went through a multi-level editorial process to provide you with the best possible quality and truly helpful information. Learn more about <html><a href="https://www.seobility.net/en/wiki/Seobility_Wiki_Team" target="_blank">the people behind the Seobility Wiki</a></html>. |
| − | seasoned SEOs, digital marketing professionals, and business experts with combined | ||
| − | hands-on experience in SEO, online marketing and web development. All our articles went | ||
| − | through a multi-level editorial process to provide you with the best possible quality and truly | ||
| − | helpful information. Learn more about <html><a | ||
| − | href="https://www.seobility.net/en/wiki/Seobility_Wiki_Team" target="_blank">the people | ||
| − | behind the Seobility Wiki</a></html>. | ||
|} | |} | ||
| + | |||
<html><script type="application/ld+json"> | <html><script type="application/ld+json"> | ||
{ | { | ||
| − | "@context": "https://schema.org", | + | "@context": "https://schema.org", |
| − | "@type": "Article", | + | "@type": "Article", |
| − | "author": { | + | "author": { |
| − | "@type": "Organization", | + | "@type": "Organization", |
| − | "name": "Seobility", | + | "name": "Seobility", |
| − | "url": "https://www.seobility.net/" | + | "url": "https://www.seobility.net/" |
| − | } | + | } |
} | } | ||
</script></html> | </script></html> | ||
Latest revision as of 18:27, 4 December 2023
Contents
What is Google Cache and how does it work?
A cache is a type of temporary memory. It allows faster access to frequently used data without having to reload every time that data is accessed. Caching is a background process, so users rarely notice it.
Google's cache contains a snapshot or stored copy of a website that can be accessed by servers and clients. This copy is created when Google's crawler analyzes a web page for indexing. Google's web crawlers continuously search for new web content in order to index it and use it for relevant search queries. Google regularly takes such snapshots of web pages. Most snapshots are taken between one and four weeks apart.
After each crawling, the current status of the respective website is analyzed in detail and then stored in Google’s cache. If a cached page is temporarily unavailable due to technical problems, clicking on a search result will display a snapshot taken from Google’s cache.
Furthermore, this cache plays a particularly important role for SERPs. Google stores the content of all websites that may be relevant to users' search queries in this cache. When answering users’ search queries, Google's server scans the cache for relevant and up-to-date web content via an index. This ensures that search queries are answered within milliseconds.
How can you check the Google Cache?
There are two ways to browse the cache for saved versions of a web page. The easiest way is to search Google for a specific website. You can then click on the small arrow next to a URL in the search results. This will open up a small drop-down menu that takes you directly to the saved version.
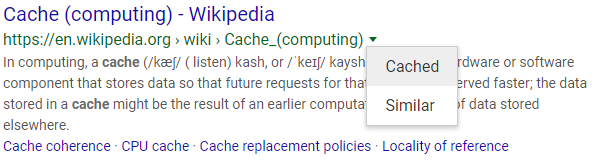
Accessing Google cache through Google search, screenshot of google.com
You can also access Google’s cache directly. However, this requires you to know the exact URL of the website you are looking for. The procedure is as follows:
Enter the following URL in the address bar of your web browser:
http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache:
After the colon you have to insert the URL of the web page you are looking for, for example:
http://webcache.googleusercontent.com/search?q=cache://example.com
Afterward, the last snapshot of the requested web page is displayed.
How to remove pages from Google Cache?
If a website has been deleted but is still displayed in Google Cache or search results, you have to remove it manually. To do this, proceed as follows:
First of all, note that only a website's owner can remove it from Google Cache in order to prevent your content from being deleted through third parties. To confirm complete control over a website, you need to set up an account in Google’s Search Console and register and confirm your website there.
You can then ask Google to delete the page from its cache and SERPs.
Advantages and disadvantages of Google Cache
The main advantage is the fast response to search queries. The caching process reduces users' waiting time, which in turn minimizes their frustration and the resulting bounce rate.
Another important advantage is that users have access to currently unavailable content. For example, if a website has been deleted by its owner, Google Cache provides backups of the most recent version and the requested content.
In addition, Google Cache allows website owners to quickly and easily check when a web page has been crawled by Google the last time. The snapshot has a timestamp that shows the exact time and date of the last indexing.
Sometimes, however, Google may not create a new snapshot while a web page is being re-indexed. An older version might be displayed in the cache and SERPs even though the content has been updated several times. For this reason, users should always be careful when using content from the Google Cache.
The advantages and disadvantages of the Google Cache summarized:
Advantages:
- Faster display of search results
- Access to content that is no longer available
Disadvantages:
- Snapshots do not always contain the latest content
Importance for SEO
In the context of search engine optimization, caching frequently updated websites has some disadvantages. Users may not find a website's most up-to-date content if Google’s cache is updated less frequently than the website itself. To avoid this problem, you can use the following meta tag:
<meta name="robots" content="noarchive">
Add this tag in the header of your web page's source code to tell search engine crawlers to not display the cached version in search results. There are also meta tags that let you specify how often a site's content is changed, so crawlers visit the page more frequently. Alternatively, you can manually report recent changes to your website. Shortly thereafter, the website is re-indexed and cached.
In addition, Google Cache can provide important insights about how relevant a website is perceived by Google. If Google attributes higher relevance to a website, it is indexed and cached more often. The timestamp in the cache shows when a website was last indexed. If a web page is cached daily, it means that Google considers it to be relevant. Such pages are re-indexed daily to provide users with a cached version that is up-to-date in the event of a problem (e.g. server failure).
Related links
Similar articles
| About the author |
 |