Cookie
Contents
Cookie – Definition & explanation
A cookie, also called an HTTP cookie or browser cookie, is data generated by a website and stored on the website user’s browser. Cookies are often stored in a small file, but some browsers store cookies in different formats.
Cookies make it possible for data, such as a user’s login credentials or items in a user’s shopping cart, to be remembered. This improves the website’s user experience. It can also help websites monitor how visitors interact with their site.
Although cookies can improve functionality and are commonly used on the web, there has been a lot of criticism on their impact on user privacy. This has led to various legal implications and is the driving factor in the introduction of cookie notices. Cookie notices require users to give a site permission to use cookies, protecting website owners from legal implications of privacy violations.
An example showing cookies stored in Firefox after navigating to a few large sites, including Amazon, Walmart, BBC news, and Google.
How cookies work
When a user opens a website or performs an action that generates a cookie, like requesting a site to remember login details, the data is sent from the website’s server to the user’s browser.
The cookie is then stored in the user’s browser for the remaining session or for a predefined timespan. Every time the browser makes a request to the server specified in the cookie, the stored data is sent to the server. This is how login details, personalization settings, and other bits of information are remembered.
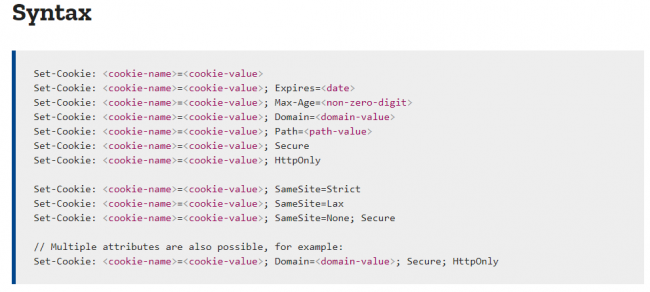
Cookie syntax provided on MDM Web Docs by Mozilla
What cookies are used for
Cookies have a variety of uses, from tracking and analytical uses to functional uses. Below are a few of the most common uses of cookies.
- Remembering login details like username and password
- Customizing content for the user
- Remembering user preferences (language, theme, etc.)
- Monitoring website traffic
- Tracking users on a website
- Tracking users across the web
Session cookies
Session cookies are cookies that are deleted after a browsing session. These cookies can prevent an eCommerce site from emptying your cart while you’re shopping or prevent you from being logged out while using a site.
Permanent cookies
Permanent cookies stay on your browser for the timeframe mentioned in the cookie. This allows websites to remember your login details or remember your preferred settings.
Third party cookies
Third-party cookies are cookies created by third-party websites, not the site a user visits. Third-party cookies generally come from advertising networks, like Google AdSense. However, certain analytics services, including Google Analytics, also require third-party cookies to function correctly.
Third-party cookies send data to a third party when the website a user is visiting makes a request to the third party’s server. They’re commonly used for cross-site tracking, allowing advertisers to track users across websites.
Since users started noticing highly personalized ads following them across sites, third-party cookies have become susceptible to criticism.
Google & third-party cookies
In 2021, Google announced they will be moving away from third-party cookies.[1] This marked the beginning of a switch towards an increased focus on user privacy on the web.
Instead of using cookies to track individual users, Google plans on grouping people based on their interests by using Federated Learning of Cohorts (FLoK)[2], eliminating the need to track individuals. This reduces the risks that come with individual tracking while still allowing advertisers to target their ads.
Cookies and privacy
Tracking website users through cookies has been a controversial topic for the past few years. Data protection laws have been enacted in many countries to protect user privacy.
The GDPR in the EU and the Data Privacy Law in the US, among many others, are examples of laws created to protect internet users’ privacy. The use of cookie notices is just one of many changes made by companies to avoid privacy violations, forcing website owners to get permission before placing cookies on a user’s browser.
Importance in SEO and marketing
Cookies are an important part of improving a website’s user experience. For example, remembering what a user adds to their shopping cart or keeping a user logged in while using a site creates a better user experience.
Cookies also help monitor how users interact with a site, making website analytics possible. New technologies, however, may find an alternative tracking method to cookies as privacy concerns continue to grow.
Understanding what cookies are and how they work allows SEOs and marketers to stay ahead of the game regarding changes made by third parties. It also helps build a better understanding of where the data used in analytics software or advertising comes from.
On top of this, cookies are an important focal point in data protection legislation around the world. Understanding what they are and how they work makes it much easier to comply with legislation and protect users’ privacy.
References
- ↑ Charting a course towards a more privacy-first web Google Ads & Commerce Blog. Retrieved 17 March 2021.
- ↑ Building a privacy-first future for web advertising Google Ads & Commerce Blog. Retrieved 17 March 2021.
Related links
- https://martechtoday.com/the-death-of-cookies-and-the-threat-to-digital-marketing-243342
- https://www.cookielaw.org/the-cookie-law/
Similar articles
| About the author |
 |