Internal Linking
Contents
What is internal linking?
An internal link is a reference to another page on the same website. It is usually implemented via page navigation or elements such as hit lists, similar articles, etc. In addition, you can link topic-relevant pages directly in a text. This provides readers with further content on certain topics right where they need it.
SEO Checker for internal linking
Check if your internal linking is optimized for search engines
Relevance
Links are one of the most important ranking factors for a website. In addition to external links (i.e. references from or to external websites), internal linking is also of great importance for search engine optimization (SEO). This is due to the fact that a large number of pages on the internet can only be accessed via internal links. Especially for subpages of very large websites, external links rarely exist, as these usually refer to the home page of a website. In such cases, internal linking can contribute to a high ranking of such pages on Google despite the lack of external links. This particularly applies to specific longtail search queries. For such search queries, you can easily achieve a high ranking through thematically relevant subpages.
Furthermore, internal links are well suited to show Google which pages of a website are most relevant (i.e. those that are most frequently linked).
In addition, you can use internal links to pass the link equity of your website from your home page to certain subpages. This means that you can transfer Google's trust in your website acquired through external links to subpages through good internal linking. Thus, in addition to internal links, external links are also of great importance for SEO in order to strengthen trust in your website and internal links. Therefore there is a close interaction of external and internal linking concerning the SEO of your website.
However, internal linking is not only relevant for SEO but can also improve the user-friendliness of your website significantly. Internal links help users to navigate on your website and can provide further information on a specific topic where it’s needed.
In summary, internal linking is relevant both for SEO and for improving user-friendliness. Therefore, it’s a topic you should definitely deal with.
Advantages of internal links
An advantage of internal links compared to external links is that you are completely flexible in terms of placement and design. You also have much freedom regarding the number of links and the use of exact-match anchor texts. The latter are not punished by Google in the context of internal linking, whereas you should be careful with exact-match anchor texts for external links in order to avoid keyword spamming. In addition, internal links are more stable and secure than external links because external links can be lost and are therefore less reliable. Another important aspect is that you can use internal links to refer to further information on a topic without harassing or deterring users.
The most important advantage of internal linking, however, is that you can use internal links to determine which subpages of your website should be important. This makes it possible to push individual pages and make their relevance clear to Google.
Optimization of internal linking
Link structure, placement, and number of internal links
Basically, the link structure of your website should be as natural and user-friendly as possible, so that users can easily navigate on your website. Google is also paying more and more attention to the user-friendliness of web pages. Therefore, you shouldn't neglect this factor in the context of SEO.
In addition, you should avoid placing too many internal links on a single page or mark such pages as an "HTML sitemap" by using the value "noindex" in the robots meta tag. When there are more than 400 links on a page, it can happen that search engines no longer follow all the links noted on that page. In addition, with each link added, less link equity per link is passed on to subpages. You should also limit the number of internal links for reasons of user-friendliness as too many links can confuse users. Instead, you should only set relevant and useful links that provide visitors with added value.
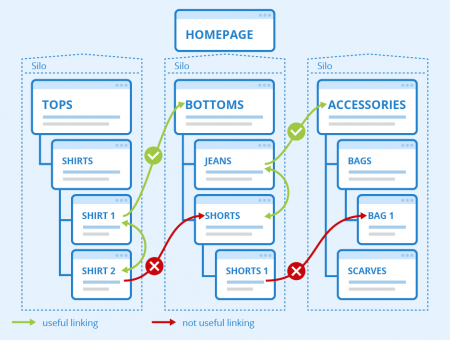
Furthermore, you should ensure a thematically relevant linking on your website, which is often referred to as siloing. According to this principle, a user who is visiting the product page of an Adidas sports shoe in an online shop should not be shown links to individual products from the "trousers" or "accessories" category, as these are highly unlikely to be relevant to him in that situation. Instead, a link to a sports shoe from Nike or Puma would be useful, since the user is obviously interested in sports shoes. You should, therefore, confine internal links to the respective category in which users are located and only refer to the start pages of other categories.
You also do not want the navigation bar of your website to contain too many links, as this can quickly get confusing for very extensive websites. Since your navigation bar should help users to navigate on your website, you should limit it to the essentials.
You should also note that if the same target page is linked several times on one page, only the first link is considered by Google. It should, therefore, be the focus of keyword optimization, since Google will tend to ignore subsequent links.
Furthermore, you should use internal links in a way that guarantees a SEO friendly site architecture where each subpage is just a few clicks away from your home page. In addition, each page should refer to thematically relevant pages or the most important main areas of your website as this leads to higher internal link popularity of the main pages.
Furthermore, you can increase the relevance of certain pages by linking them directly in a thematically relevant text. This is also helpful for users who are reading this text, as they no longer have to search for further information.
Your internal links should have the following characteristics in order to be classified as important by Google:
- placement in the main area of a page (not in the footer or sidebar)
- placement at the beginning of a text
- visual highlighting (by using colors, underlinings etc.)
- relevance of the link target for the page on which the link is set
- high number of visitors to the site
- limited number of links on a page
Anchor text
Anchor texts are particularly important elements for the SEO of internal linking, which you shouldn’t forget about. Anchor texts should provide a short but meaningful description of the content of the linked page. You should avoid meaningless anchor texts that do not give any information about what to expect on the target page because these are rarely clicked. In addition, your anchor texts should contain the most important keywords for the linked page (if possible at the beginning), since Google uses anchor texts for the thematic classification of the linked page. However, you should avoid the excessive use of keywords, as this does not provide any added value to users and is therefore rated negatively by them.
Furthermore, anchor texts should not be too long or repeated too many times, as Google punishes the frequent repetition of anchor texts. You also should avoid using the same anchor texts for different target pages, as otherwise there will be thematic overlaps between these pages and in consequence they are not indexed specifically enough. In simple terms, this means that Google does not know which page should be linked to a particular keyword so that several pages of a website compete with each other. This leaves important SEO potentials of internal linking unused. For this reason, you should already define anchor texts for each subpage when planning your website.
Generally, you should avoid trivial link texts such as "show more" or "read more", as search engines don’t pay as much attention to them as to keyword anchor texts.
Other
If you want to use image links, you should choose the ALT attribute and image title carefully, since no link text is available here that search engines can evaluate for indexing the link target.
In addition, so-called breadcrumbs (secondary navigation) are a simple means for generating internal links and link equity for SEO.
Screenshot with breadcrumbs on seobility.net
Furthermore, you should avoid using internal nofollow links for SEO as otherwise no link equity can be transferred to the linked pages. This valuable link equity is also lost if internal links refer to non-existing pages or pages with redirects.
Practical tips
Internal linking is a very important and extensive part of SEO and there are many points to consider in order to make use of the SEO potential of your website. Therefore, we have put together a few practical tips to help you get started with this topic.
Check existing content
When you publish new SEO content (e.g. a new blog post), you should always check your existing content for possibilities to link the new post. By doing this, you can easily create relevance for your new page, which eventually leads to a high ranking.
Use HTML sitemaps
Using an HTML sitemap ensures that each subpage is only two clicks away from your home page, thus creating an SEO friendly website architecture. For example, for an online job portal, a bar with all letters of the alphabet is a good choice, allowing you to call up any city with just a few clicks using its initial letter.
Have your website tested
In order to check the quality of your internal linking, you should consider asking a person who is not familiar with your website to search it for specific information. From how difficult or easy this is for them, you can deduce whether your website is already clearly and sensibly linked or whether there’s still need for optimization. This is a very simple method to uncover weak points that you wouldn't notice yourself, because you already know your own website perfectly.