Difference between revisions of "HTTP Status Code"
Ralph.ebnet (talk | contribs) |
(→Similar articles) |
||
| Line 92: | Line 92: | ||
[[Category:Web Development]] | [[Category:Web Development]] | ||
| + | |||
| + | {| class="wikitable" style="text-align:left" | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | |'''About the author''' | ||
| + | |- | ||
| + | | [[File:Seobility S.jpg|link=|100px|left|alt=Seobility S]] The Seobility Wiki team consists of seasoned SEOs, digital marketing professionals, and business experts with combined hands-on experience in SEO, online marketing and web development. All our articles went through a multi-level editorial process to provide you with the best possible quality and truly helpful information. Learn more about <html><a href="https://www.seobility.net/en/wiki/Seobility_Wiki_Team" target="_blank">the people behind the Seobility Wiki</a></html>. | ||
| + | |} | ||
| + | |||
| + | <html><script type="application/ld+json"> | ||
| + | { | ||
| + | "@context": "https://schema.org", | ||
| + | "@type": "Article", | ||
| + | "author": { | ||
| + | "@type": "Organization", | ||
| + | "name": "Seobility", | ||
| + | "url": "https://www.seobility.net/" | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | } | ||
| + | </script></html> | ||
Latest revision as of 16:11, 6 December 2023
Contents
Definition of HTTP status code
An HTTP status code is a code that indicates the status of an HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol) request. They are sent to the client by the server in response to a resource request.
HTTP status codes follow a standard format and indicate whether a server request was successful, unsuccessful, or whether something else happened after the request was made, like a redirect to another page/resource.
An image of Nike’s 404 page is shown when a 404 status code is provided, indicating that the page doesn’t exist.
What are HTTP status codes used for?
An HTTP status code lets the browser know how the request made by the client went. It may indicate that the request was successful, but it can also indicate that the request was unsuccessful or provide other information, such as if the visitor was redirected to another page. The server provides this information in response to the resource request in the form of a response code.
This helps indicate what the problem was, allowing users to react accordingly. This also provides search engine crawlers with this same information, allowing them to remove a page from their index if it has moved or has become unavailable and add crawlable pages to their index.
Status codes in SEO
There are a large number of response status codes, each reflecting a different event. There are five main categories, each with various response status codes. Below is an overview of the main status codes and their effect on SEO.
It’s common practice to add “XX” to the end, referring to all status codes within this category. For example, 4XX status codes refer to all HTTP status codes starting with 4, like 404 and 403.
1XX
1XX status codes are informational status codes and aren’t that relevant for SEO. They indicate that all is well so far and that the resource request was received by the server. An example is the 100 code, which indicates that the first part of a request was received and that the client can continue sending the request.
2XX
2XX response codes indicate that a request was successful, indicating that a resource was requested and served successfully. If the crawling/indexing of these pages isn’t blocked elsewhere, like in the robots.txt file, these pages/resources can be indexed by search engines. An example is the 200 response code which means that the request was successful.
3XX
3XX response codes signal a redirect, which can be either temporary or permanent. This sends users to the correct URL and helps search engines understand that the page still exists, but has moved to a different location.
Understanding 3XX redirects, like the 301 redirect and 302 redirect, is important for SEO. The 301 redirect is used to indicate that a resource has moved permanently. It will send users to the new location and tells search engines to treat the new page the same as the old page.
301 redirects transfer “link juice” to the new page, preserving the SEO value. This allows websites to change their URL structure and merge pages without it negatively affecting their SEO performance.
The 302 redirect is used less often and indicates a resource has moved temporarily. This redirect is used when the old URL will be used again in the future. For example, when a website is being redesigned or when running a seasonal offer.
A 302 redirect won’t pass link equity. However, if the page serves a 302 server response code for a long time then it may be treated in the same way as a 301 by search engines.
Redirect chains
When redirecting a page using a 3XX redirect, an extra server request is required. This can impact website loading speed. If there are multiple redirects, for example, page A redirects to page B, page B to page C, and page C to page D, then this can cause loading issues.
Since link equity is lost and loading speed is slower, these redirect chains can also harm a page’s SEO performance.
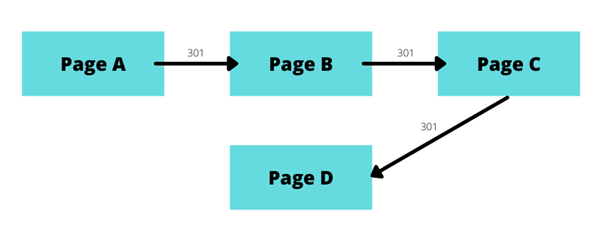
Example of a redirect chain with 301 redirects.
4XX
4XX status codes indicate an error on the visitor’s side, telling the client that the resource request was unsuccessful. They indicate that a page isn’t loading. Each status code represents a different reason why the request was unsuccessful.
4XX errors tell search engine crawlers and users that the page/resource isn’t loading. This can help search engines understand that a page no longer exists, saving your crawl budget by showing search enginesthey no longer need to crawl the page. If this error is often shown when the page does exist, it can cause a page to be removed from the SERPs.
403
The 403 forbidden error tells the user or search engine that they are not authorized to view the page. This prevents users from viewing the page and blocks search engines from crawling it. If this error is shown on a page, the page will not be crawled or indexed.
404
The 404 response code is shown when a page/resource can’t be found. It tells users and crawlers that the page no longer exists at this destination. In SEO, 404s are used to indicate that a page no longer exists. This tells search engines that the page can be removed from the index and no longer has to be crawled, freeing up crawl budget for existing pages.
410
The 410 indicates that a page no longer exists. This is seen as more permanent than the 404 error. 410 response codes signal to search engines that the page shouldn’t be crawled or indexed.
5XX
5XX response codes indicate server errors, telling the client that the request was unsuccessful. This code signals that something went wrong on the server’s side, preventing the page from loading. 5XX errors can be caused by server downtime, but also by other issues with the server. 5XX errors can be very harmful to a site’s SEO performance.
An example is the 500 response code, which indicates that there was an unexpected internal server error that prevented it from being able to fulfill the request.
The importance for SEO
Understanding the different HTTP status codes will allow you to better optimize your website. Since these server response codes are important for how both users and search engines interact with your site, they provide you with more control over the user experience.
Related links
Similar articles
| About the author |
 |